
Understanding Anaesthesia Machine: Uses, Purpose and its Components
- Published By The Statesman For The Statesman Digital
- 5 months ago
An anesthesia machine is a pneumatic device that delivers a controlled mixture of oxygen, gases, and anesthetic agents to a patient, enabling them to remain unconscious and breathing during surgery, while also facilitating ventilation and monitoring vital signs.
Here's a breakdown of its uses and key components
Uses:
-
Delivering Anesthesia:The primary function is to deliver a precise mixture of anesthetic gases and oxygen to the patient, inducing and maintaining unconsciousness.
-
Ventilation:The machine can assist or control the patient's breathing, ensuring adequate oxygenation and carbon dioxide removal.
-
Monitoring:It incorporates monitors to track vital signs like heart rate, blood pressure, oxygen saturation, and end-tidal CO2 levels.
-
Safety:It helps minimize anesthesia-related risks to patients and staff by accurately controlling gas flow and concentrations, and incorporating safety features like alarms and pressure relief valves.

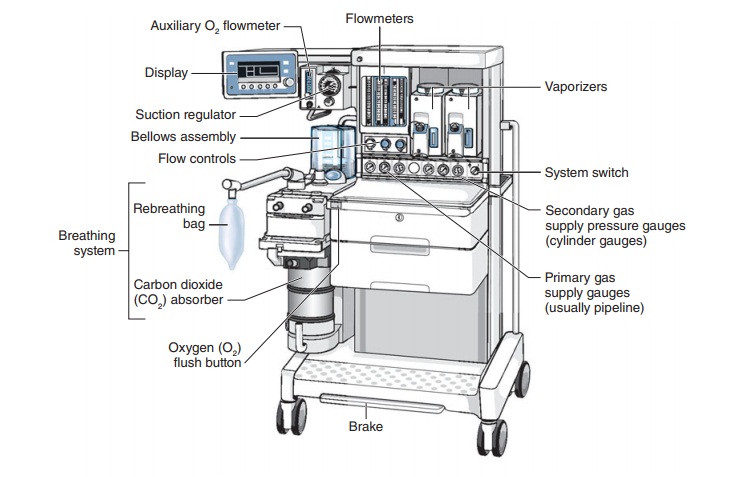
Key Components:
-
Gas Supply:
- Oxygen Source: A central pipeline or pressurized cylinders provide oxygen.
- Nitrous Oxide: Another gas used in anesthesia, also supplied from cylinders or pipelines.
- Air: Medical air is also supplied, often from a central pipeline.
- Oxygen Source: A central pipeline or pressurized cylinders provide oxygen.
-
Pressure Regulators:These reduce the high pressure of gases from cylinders or pipelines to a lower, safe level.
-
Flowmeters:These devices precisely control and measure the flow of each gas (oxygen, nitrous oxide, air).
-
Vaporizers:These convert liquid anesthetic agents into a vapor for inhalation.
-
Breathing Circuit:
- Tubing: Connects the machine to the patient, allowing for gas delivery and exhaled gas to be channeled.
- Valves: One-way valves ensure proper gas flow and prevent backflow.
- CO2 Absorber: Removes exhaled carbon dioxide.
- Ventilator: Provides mechanical ventilation if needed.
- Tubing: Connects the machine to the patient, allowing for gas delivery and exhaled gas to be channeled.
-
Scavenging System:This system removes excess anesthetic gases from the breathing circuit to prevent environmental pollution and protect healthcare workers.
-
Monitors:
- Oxygen Concentration Monitor: Ensures adequate oxygen levels in the delivered gas mixture.
- End-Tidal CO2 Monitor: Measures carbon dioxide levels in exhaled breath.
- Anesthetic Concentration Monitor: Tracks the concentration of anesthetic gases delivered to the patient.
- Vital Signs Monitors: Display heart rate, blood pressure, and other vital signs.
- Oxygen Concentration Monitor: Ensures adequate oxygen levels in the delivered gas mixture.
Share on
SHARE YOUR COMMENT
MORE STORIES FOR YOU
Trending Stories
DJ Mo’s former illicit lo...
- Published By Jane
- January 15, 2024
Mapenzi! Zari and Tanasha...
- Published By Jane
- October 24, 2023
Zuchu Speaks on Diamond P...
- Published By Jane
- October 12, 2023
Hio Ni Upumbavu Wasituche...
- Published By Jane
- November 8, 2023
RECOMMENDED FOR YOU
Your Lungs Hold Secrets A...
- Published By The
- September 11, 2025
Better Sleep?: See The Li...
- Published By The
- September 11, 2025
What to Know About iPhone...
- Published By The
- September 11, 2025
From Teacher to Mwalimu N...
- Published By The
- September 11, 2025
Latest Stories
Champions League: Arsenal...
- Published By The
- October 2, 2025
"Sura Kama Ya Kiatu": Bet...
- Published By The
- October 2, 2025
The Reason Diana Marua is...
- Published By The
- October 2, 2025
Shock as Audit Reveals Mi...
- Published By The
- October 2, 2025



